Galaxy: A Vast System of Stars and Celestial Objects
Galaxy refers to a large system of stars, gas, dust, and other celestial objects bound together by gravity. It is a fundamental unit of the universe and there are billions of galaxies in the observable universe. Our own galaxy, the Milky Way, is just one of many galaxies that exist. Galaxies vary in size, shape, and composition, and they can contain anywhere from millions to trillions of stars. They are fascinating objects that astronomers study to understand the structure and evolution of the universe.
What is Galaxy? PDF Free Download
A galaxy is a vast system of stars, stellar remnants, interstellar gas, dust, dark matter, and an important part of the universe. Galaxies are held together by gravity and can contain billions of stars. The Milky Way is the galaxy that encompasses our solar system. It is spiral in shape and contains approximately 100 billion stars. There are different types of galaxies, including spiral, elliptical, and irregular galaxies.
What is a Galaxy?
Definition of a galaxy
A galaxy is defined as a gravitationally bound system of stars, stellar remnants, interstellar gas, dust, dark matter, and other celestial objects. It forms a major part of the universe, and there are billions of galaxies in the observable universe.
Types of galaxies
Galaxies come in various forms, including spiral galaxies that have a disk of stars and interstellar medium with spiral arms, elliptical galaxies which are generally ellipsoidal or spherical in shape, and irregular galaxies that lack a distinct regular form. The classification is based on their shape, structure, and stellar content.
Formation of galaxies
Galaxies are thought to have formed from the gravitational collapse of gas, dust, and dark matter. The precise mechanisms of their formation are still the subject of ongoing research and debate, but they are believed to have come into existence billions of years ago.
Study of Galaxies
Research on galaxies by NASA
NASA, the US space agency, has been actively involved in studying galaxies through various missions and space observatories. The exploration of galaxies and their properties remains a major focus of NASA’s research endeavors.
Role of space telescopes in galaxy study
Space telescopes, such as the Hubble Space Telescope and the upcoming James Webb Space Telescope, have played a crucial role in observing and studying galaxies. They have provided valuable insights into the formation, evolution, and characteristics of galaxies.
Understanding the Milky Way galaxy
Studying the Milky Way galaxy, our home galaxy, has been instrumental in gaining a better understanding of the structure, composition, and dynamics of galaxies. The Milky Way serves as a reference point for the study of other galaxies.
Galaxies and Black Holes
Supermassive black holes in galaxies
Many galaxies, including the Milky Way, are believed to harbor supermassive black holes at their centers. These extremely dense regions exert a significant influence on the surrounding stars and interstellar material within the galaxies.
Impact of black holes on galaxy formation
The presence of black holes in galaxies can have a profound impact on their formation and evolution. The gravitational effects and energetic processes associated with black holes play a crucial role in shaping the properties of galaxies.
Galaxies and the presence of gas and dust
Gas and dust are essential components of galaxies, contributing to the formation of new stars and providing the raw material for the interstellar medium. They are fundamental in shaping the dynamics and evolution of galaxies.
Galaxy Formation and Evolution
How galaxies form and evolve
Galaxies form and evolve through a complex interplay of gravitational interactions, gas accretion, star formation, and feedback processes. Their evolution over billions of years is a dynamic and ongoing phenomenon that continues to be a subject of scientific inquiry.
Galaxies in the early universe
The study of galaxies in the early universe provides insights into their formation and development, offering a glimpse into the conditions that existed during the early stages of cosmic history, within millions of years after the Big Bang.
Formation of new stars in galaxies
New stars continuously form within galaxies as a result of the gravitational collapse of interstellar gas and dust clouds. The process of star formation is fundamental to the evolution and rejuvenation of galaxies.
The Milky Way Galaxy
Characteristics of the Milky Way galaxy
The Milky Way galaxy is a barred spiral galaxy that spans about 100,000 light-years across. It contains billions of stars, including our sun, and hosts a complex interstellar environment composed of gas, dust, and stellar remnants.
Comparison with other types of galaxies
Compared to other types of galaxies, such as elliptical and irregular galaxies, the Milky Way exhibits unique features and structural characteristics that make it a subject of intensive study and fascination for astronomers and cosmologists.
Galaxies in relation to the Milky Way
In the vast cosmic landscape, the Milky Way is just one among billions of galaxies. Its interactions with neighboring galaxies and cosmic structures provide valuable insights into the broader context of galactic dynamics and evolution.
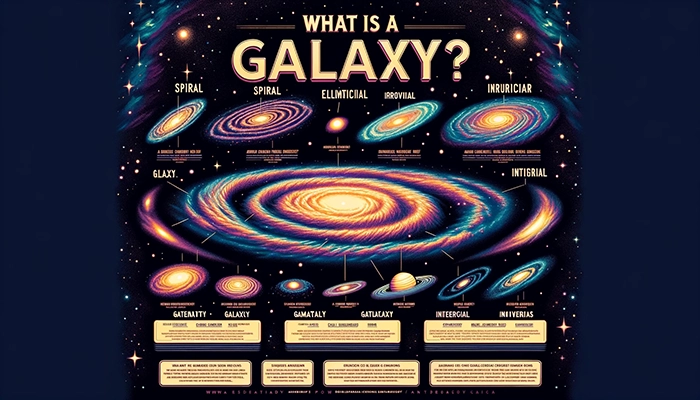
Q: What is a galaxy?
A: A galaxy is a system of stars, stellar remnants, interstellar gas, dust, dark matter, and other objects bound together by gravity.
Q: How many galaxies are there in the universe?
A: Current estimates suggest that there are billions of galaxies in the observable universe.
Q: What are the main types of galaxies?
A: The main types of galaxies are elliptical, spiral, and irregular. These categories are based on their visual appearance.
Q: What are dwarf galaxies?
A: Dwarf galaxies are small galaxies that typically contain thousands to millions of stars. They are much smaller and fainter than larger galaxies.
Q: How do galaxies form?
A: Galaxies are believed to have formed from the gravitational collapse of clouds of gas, and they continue to evolve over billions of years.
Q: What are some examples of galaxies?
A: Examples of galaxies include the Milky Way, the Andromeda Galaxy, and various dwarf galaxies within our local group.
Q: Can galaxies collide?
A: Yes, galaxies can collide and merge with one another over long periods of time due to gravitational interactions.
Q: What is the approximate age of the universe’s galaxies?
A: The universe’s galaxies are thought to have started forming around 13.5 billion years ago, not long after the Big Bang.

























